Fixed Sports Betting – Extortion Victims: Prince Andrew – To Julian Assange – Rose McGowan, Prince Harry & Michael Jackson – British Broadcasting Company Exposed In Global Prosecution – Running Blackmail Ring – Child Sex Abuse Materials Coverup & Fixed Sports Betting & UK MP Scandals Cover Up

The report assesses governance, safeguarding, and omission-liability exposure for public-service broadcasters—particularly the BBC—once constructive notice is established through live proceedings, public filings, and discoverable records.
As procedural records approach fixation on January 16, 2026, the analysis identifies a clear risk escalation point under UK law, Ofcom duties, and established case law (Flood, Lachaux, Reynolds), where failure to rebalance context may convert editorial discretion into reviewable omission.
Public-interest risk analysis. Not findings of criminal guilt. Presumption of innocence applies.
Criminal Counts Asserted in Live Filings (Matters of Record)
Multiple court filings and regulatory submissions now expressly assert criminal counts and statutory violations, including but not limited to:
- Child sexual exploitation and safeguarding offences
- Conspiracy and racketeering-related statutes
- Sports betting manipulation and gambling fraud
- Obstruction, coercion, and blackmail-related offences
These criminal counts are asserted as pleaded facts within live proceedings and formal complaints before courts and law-enforcement agencies in multiple jurisdictions. They are not journalistic conjecture.
While no court has yet adjudicated these counts to final judgment, their existence in filed pleadings establishes constructive notice for media entities, regulators, and public institutions.
Risk Trigger: Once criminal counts are formally asserted in court filings, continued allegation-dominant coverage without procedural context may expose broadcasters to omission-based liability under UK law.
Now indexing alongside BBC’s own “InDepth” analysis, this independent analyst report examines a systemic media-coercion risk architecture arising when live court filings, pleaded criminal counts, and regulatory complaints coexist with allegation-dominant coverage absent procedural context.
ANALYST ALERT
Systemic Media-Coercion Risk Architecture
Public-Service Broadcasting • Safeguarding • Omission Liability
Prepared for: Public-Interest Review, Regulators, Parliament, Courts
Scope: Risk Architecture & Governance Exposure — Not Findings of Criminal Guilt
Procedural Record Fixation Countdown
EASTERN CARIBBEAN SUPREME COURT
January 16, 2026 • 9:00 AM AST
LIVE PROCEEDINGS • CONSTRUCTIVE NOTICE ESTABLISHED
Executive Summary
This briefing identifies a foreseeable systemic media-coercion risk architecture operating within highly concentrated media ecosystems. The risk crystallizes where allegation-dominant coverage, legacy safeguarding failures, and omission of adjudicative context intersect — particularly for public-service broadcasters.
This document does not allege criminal guilt. It assesses institutional exposure under UK law, Ofcom duties, and public-service standards once constructive notice exists through live proceedings, public filings, and regulatory engagement.
Core Analytical Thesis
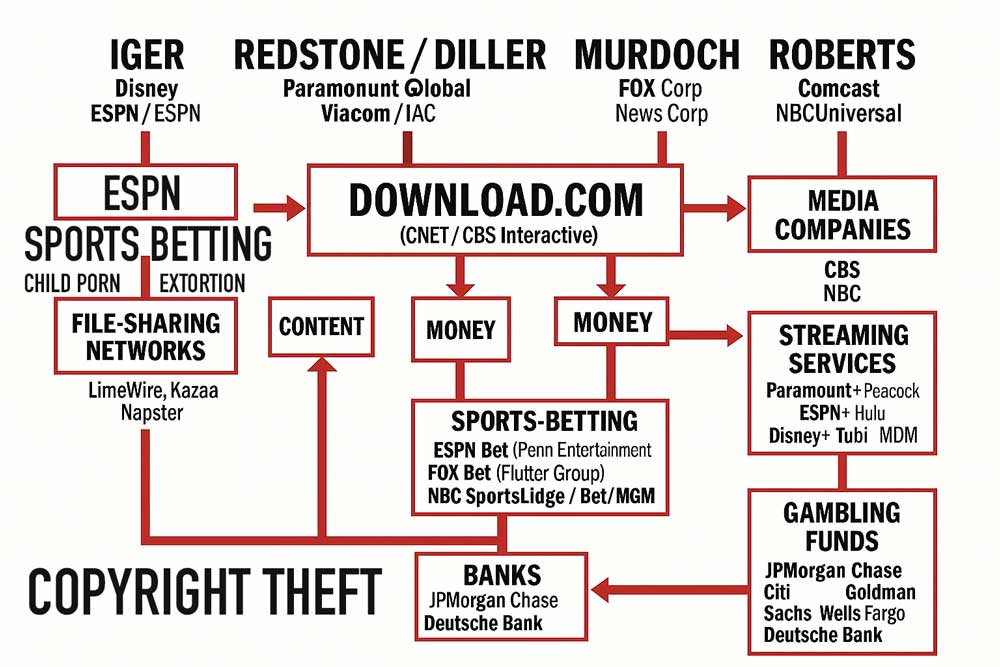
Across multiple jurisdictions (UK, United States, Caribbean), public records, inquiries, and live court filings repeatedly surface the same structural pattern:
- Consolidated control of media distribution and narrative amplification
- Historic digital exploitation pipelines with residual safeguarding exposure
- Fixed sports-betting and gambling inducement ecosystems
- Reputational destruction decoupled from criminal adjudication
Individually, these factors raise concern. Together, they create a coercive leverage environment capable of inflicting severe reputational and psychological harm without any criminal conviction.
Key Risk Vectors (Documented, Not Accusatory)
1. Legacy Child-Protection Exposure
Historic exploitation of commercial digital platforms (pre- and post-P2P era) leaves enduring risk via residual logs, delayed takedowns, and jurisdictional fragmentation — creating uniquely coercive leverage even decades later.
2. Fixed Sports Betting & Gambling Inducement
Offshore betting structures, opaque sponsorships, and historic organized-crime revenue models enable non-transparent financial pressure pathways insulated from scrutiny.
3. Media Amplification & Omission
Concentrated media reach allows allegations to dominate public consciousness while acquittals, dismissals, or non-conviction posture receive materially less prominence — a known vector of serious reputational harm.
Illustrative Exemplar Pattern — UK & International
No Findings of Criminal Guilt
The individuals below are referenced solely to illustrate reputational harm absent criminal conviction. Inclusion reflects publicly documented outcomes (acquittal, no charge, dismissal, or settlement without admission).
United Kingdom
- Prince Andrew — Civil settlement; no criminal charges or convictions
- Sir Cliff Richard — Never charged; BBC apologised and paid damages for unlawful coverage
- Paul Gambaccini — Arrested, no charges; compensation paid; cited in post-Savile reviews
- Christopher Jefferies — Wrongly portrayed; libel claims upheld against UK press
- Sir Edward Heath — Posthumous allegations; official review found no substantiated criminal case
- Julian Assange — No conviction for sexual offences; prolonged allegation-dominant coverage
- Prince Harry — No criminal allegations; extensive litigation over coercive media practices
International Comparators
- Michael Jackson — 2005 acquittal; no criminal conviction; posthumous narrative persistence
- Alki David — Civil litigation only; no criminal convictions on core allegations
- Kanye West — Pending civil claims; no criminal convictions
- Rose McGowan — No criminal conviction; documented retaliatory reputational exposure
The unifying factor is not guilt, but the operation of amplification mechanics combined with omission of adjudicative context.
BBC Public-Service Exposure
As a Royal Charter broadcaster, the BBC carries a heightened duty once placed on constructive notice through:
- Live proceedings and default judgments (e.g. Antigua & Barbuda — ANUHCV2025/0149)
- Regulatory engagement and safeguarding reviews
- Documented historical failures (Savile era) requiring caution against over-correction
At this stage, continued omission of context may convert editorial discretion into reviewable omission, engaging negligence-based exposure under UK law.
Applicable UK Case Law
- Lachaux v Independent Print — Serious harm via implication and repetition
- Flood v Times Newspapers — Duty to reassess as facts evolve
- Reynolds v Times — Proportionality, verification, public interest
- Jameel v Wall Street Journal — Avoidance of unnecessary reputational harm
January 16, 2026 — Risk Escalation Point
Once procedural records fix and defaults are adjudicated, omission risk becomes foreseeable rather than speculative. Post-judgment, failure to rebalance coverage may materially elevate institutional exposure.
Presented as an analytical framework—not an accusation—the report maps recurring patterns observed in regulatory filings, public inquiries, and historic media scandals, highlighting systemic weaknesses where governance, safeguarding, and financial incentives intersect.
